
If the Taliban Can Do It, So Can We
The Taliban retook power in Afghanistan after the U.$. retreat in August 2021.(1) In April 2022, the Taliban once again instituted a ban on poppy cultivation, and by December 2023 they had reduced production by 95%. Most global poppy cultivation now takes place in unstable regions of Myanmar.(2) The Taliban banned opium production with similar results in 2000, but when the United $tates invaded Afghanistan in 2001, they saw to it that opium production was restored and there were continued increases up until last year. As a very poor country, poppy production is a significant cash crop for Afghan farmers. Still the Taliban has been able to enforce the ban, while working with farmers to grow alternative crops. The United $tates says they spent $8 billion trying to eradicate poppy during their rule over the country from 2001 to 2018.(2)
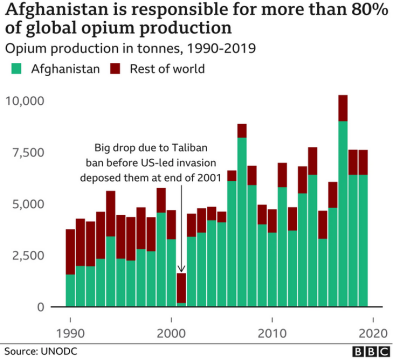
Afghanistan has been negotiating agricultural deals with China since the Taliban regained power in 2021, and are scheduled to begin shipping large exports of produce to China this month [December 2023]. Afghanistan has attended China’s recent Belt and Road Forum, with China becoming Afghanistan’s second biggest trade partner after neighboring Pakistan.(3) This growing export of raw materials has come with far greater imports of products from social-imperialist China, that will feed a relationship of unequal exchange leading to wealth transfer out of Afghanistan. But in the short-term it is helping provide economic options other than exporting opium to Europe, where Afghanistan had provided 95% of the black market supply.(4)
While the United $tates invaded Afghanistan shortly after the 9/11 attacks, by 2003 they had begun a full-scale invasion of Iraq using 9/11 as a cover once again. Iraq had also had a culture and tradition that made drug use relatively uncommon. This began to change since the overthrow of the Ba’ath Party in 2003, with sharp increases in crystal meth and the stimulant Captagon documented since 2017.(5) It’s also interesting to note that besides U.$. oil interests, Amerikans were concerned with the ruling Ba’ath Party’s support of certain militant groups in Palestine.
Of course a better example of eliminating opium is China, where the masses were the victims of British Opium War. The Taliban isn’t fighting addiction so much as they are trying to shift agricultural production in a way that is challenging the incomes of poor farmers. The Chinese Communist Party (CPC) gives us a better model than the Taliban of how to fight addiction by empowering the masses through socialism from 1949-1976. We wrote about this in Issue 59 on drugs:
“Richard Fortmann did a direct comparison of the United $tates in 1952 (which had 60,000 opioid addicts) and revolutionary China (which started with millions in 1949).(9) Despite being the richest country in the world, unscathed by the war, with an unparalleled health-care system, addicts in the United $tates increased over the following two decades. Whereas China, a horribly poor country coming out of decades of civil war, with 100s of years of opium abuse plaguing its people, had eliminated the problem by 1953.(9) Fortmann pointed to the politics behind the Chinese success:
“If the average drug addiction expert in the United States were shown a description of the treatment modalities used by the Chinese after 1949 in their anti-opium campaign, his/her probable response would be to say that we are already doing these things in the United States, plus much more. And s/he would be right.”(9)
“About one third of addicts went cold turkey after the revolution, with the more standard detox treatment taking 12 days to complete. How could they be so successful so fast? What the above comparison is missing is what happened in China in the greater social context. The Chinese were a people in the process of liberating themselves, and becoming a new, socialist people. The struggle to give up opium was just one aspect of a nationwide movement to destroy remnants of the oppressive past. Meanwhile the people were being called on and challenged in all sorts of new ways to engage in building the new society.”(6)
Here we see the United $tates failing where socialist China succeeded, using the exact same tools! These historical examples demonstrate that the principal contradiction behind the drug epidemic is found within the structure of society and not with specific treatment techniques. China was also a divided, drug-ravaged population coming into the war of liberation, proving how a new culture can be built and a people can rise above addiction.
But wait, the Taliban and the CPC both had state power when they eliminated drugs. True. And the people in state power in the United $tates are not interested in empowering the people. Instead, they continue to allow the free flow of drugs into even the most controlled environments. On the road to state power, the CPC built dual power, by developing liberated zones in China where they could begin to experiment with the policies and practices of building socialism, including the elimination of drug use.
U.$. prisons are very different conditions than the Chinese countryside. And communists are far from state power in this country. But comrades must use the materialist method to develop strategies for building forms of dual power and transforming the culture of the oppressed to fight drug addiction. The Revolutionary 12 Steps that we published last year is one tool for that, but the real challenge is putting programs into practice. We must build independent institutions of the oppressed that combat addiction by empowering people in a greater liberation struggle. It is the plague of hopelessness that is truly killing us.
NOTES:
1. Plastick, October 2021, Whither Afghanistan?,
Under Lock & Key Issue 75.
2. CBS
News, 12 December 2023, Myanmar overtakes Afghanistan as the world’s
biggest opium producer, U.N. says.
3. Ralph
Jennings and Mandy Zuo, 7 November 2023, CIIE: China, Afghanistan
cultivate deeper ties with agriculture deals, South China Morning
Post.
4. BBC News, 25 August
2021, Afghanistan: How much opium is produced and what’s the Taliban’s
record?
5. Jamal
Muzil, May 2023, Substance abuse in Iraq, Quantifying the Picture,
Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology
30(12):302-313.
6. Wiawimawo,
November 2017, Opioids on the Rise Again Under Imperialism, Under Lock
& Key Issue 59.
Related Articles:







